Start Healing with Neurotherapy and the Support You Need
We are here to help you with the treatments for the toughest medical challenges through our recognized expertise.
Our Treatments

1. Abdominal Disorder
Problem
The conditions included in abdominal disorders can be mild or serious and involve the organs and tissues such as the gallbladder, intestines, liver etc.
Symptoms
Nausea and vomiting, unexplained loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss or gain, constipation, bloating, diarrheoa, heartburn, fever and fatigue.

2. Sciatica
Problem
Sciatica is a nerve root disorder. Nerve roots project from the spinal cord, delivering signals to and receiving signals from almost all parts of the body. These nerve roots emerge from the spinal column through openings between vertebrae.
The most common cause of nerve root damage is a ruptured disk between vertebrae. When nerve roots in the lower back are under pressure, pain may be felt only in the lower back; or the pain may travel along the sciatic nerve to the buttocks, thigh, calf and foot. This pain is called sciatica.
Symptoms
Sharp pain running from the lower back down to the feet, numbness along the sciatic nerve, hip pain, burning and tingling sensations and difficulty in moving legs.

3. Arthritis
Problem
Arthritis causes pain and stiffness in the joints. Pyogenic Arthritis is the dominating type where bacteria penetrate through a wound or reach the joint through the bloodstream, which results in fever, pain and a swollen joint.
Symptoms
Joint pain, fatigue, fever, weight loss, stiffness, swelling, skin rashes, weakness, numbness and more according to the type.

4. Asthma (Bronchial Asthma)
Problem
Generally, stress or allergy results in bronchospasms triggered by Asthma. Here, the muscles in the bronchial tubes go into spasm and make the tubes narrow. Though it occurs in any season but worsens in summer. Asthma gets precipitated by allergies, wind, cold, fog or a sudden change in the temperature.
Symptoms
Trouble while breathing out. Breathlessness, wheezing while breathing, restlessness, sneezing, drowsiness, irritability, dry or irritant cough and attacks (in severe cases). However, an attack usually occurs suddenly in the middle of the night and the person feels oppression in the chest and difficulty in breathing.

5. Colitis
Problem
A person with an inflammation of the large intestine faces Colitis. Some of the causes of Colitis include stress, emotional tensions, overfeeding, excessive sugar consumption, hasty drinking of milk and improper digestion. In Ulcerative Colitis, the lining of the intestine gets infected, while in Mucous Colitis (the chronic non-inflammatory disease), excess mucus gets secreted with disordered colonic motility.
Symptoms
Diarrheoa and dehydration, passing blood in the stool, fever and abdominal pain are the symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis. Pain, constipation and diarrheoa with the passage of mucus are the symptoms of Mucous Colitis. Other symptoms of Colitis are weight loss due to difficulty in absorbing nutrients, a feeling of incomplete evacuation even after passing stool, fatigue and cramping.

6. Paralysis
Problem
Paralysis is the complete or partial loss of ability to move a body part. It results from damage to the motor nerves or the brain or spinal cord. In a rare case, it can result from damage to the muscle itself. Damaged sensory nerves result in loss of sensation in the affected area.
Symptoms
Loss of muscle function, difficulty speaking, numbness or weakness in the affected area, vision changes, no control over bladder and bowel and tingling. These symptoms depend on the type of paralysis and the area affected by it.

7. Epilepsy
Problem
Epilepsy is attacks of convulsions of cerebral origin. It is also defined as a condition characterised by recurrent episodes primarily of cerebral origin in which there is disturbance of movement, sensation, behaviour or consciousness. Episodes begin suddenly and have a tendency to disappear spontaneously.
In minor epileptic attacks, the patient may become pale with eyes fixed and may become momentarily unconscious. He/she may then resume his/her previous activities as though nothing has occurred. The condition may resemble a fainting attack, with a fall in blood pressure which may be sudden, following fright, bad news, a horrifying sight or pain or may be gradual, when there has been debilitating illness, fatigue, or long periods of sitting or standing in a hot stuffy atmosphere.
When a person feels faint, get his head down quickly. Lay him down with the head lower than the feet. On recovery, give sips of water, tea or other beverage.
In a major epileptic attack, patients feel a sense of strangeness accompanied by headache, irritability, restlessness or a feeling of lethargy. He/she suddenly loses consciousness, falls to the ground and remains rigid for some seconds with flushed face. He/she may bite the tongue, may pass urine and/or motions involuntarily. After a few minutes, convulsions may cease and he may behave in strange manner. Place the handle of a spoon or any other hard object rapped in a handkerchief between his back teeth to prevent the patient from biting his tongue.
Some times an epileptic attack may be due to sugar reduction or due to reduction of sodium.
Symptoms
During an attack, the person’s eyes get fixed, they become pale, momentarily get unconscious, may pass urine, might bite off their tongue and within a few moments, they might resume working as if nothing happened. An episode might resemble a fainting attack and a sudden fall in the blood pressure.

8. Parkinson’s Disease
Problem
Parkinson's disease progresses slowly. It is a degenerative disorder that affects the central nervous system and primarily damages parts of the brain stem. Thus, the person cannot control movement, balance and posture. Damage to the dopamine-producing neurons, protein clumps in the brain, exposure to specific toxins, genetics and inflammation in the brain are the causes of Parkinson’s Disease.
Basal Ganglia lies deep within the brain and has a neurotransmitter called ‘dopamine.’ The nerves in the Basal Ganglia degenerate but the underlying cause is unknown.
Symptoms
Tremors (shaking movement), muscle stiffness, slow movements, postural instability, speech problems, writing difficulties, bladder problems, dementia (in some cases), a staring look, speaking softly in a monotone and more according to the type of disease.
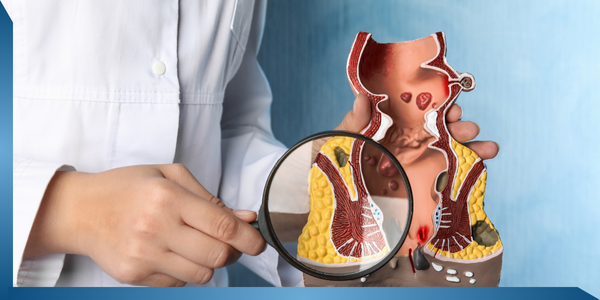
9. Piles
Problem
Piles (haemorrhoids) are dilated veins in the rectum. These swollen veins can affect varicose veins in the legs. Depending on the plexus of the veins affected, piles may be internal or external.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of piles include feeling full even after having passed stools; discomfort or pain around the back passage; bright red blood on stool; irritation around the anus or a lump next to the anus.

10. Depression (Melancholia)
Problem
Melancholic person has depressed personality. Such a person has a depressed, pessimistic outlook and philosophy and may show suicidal tendencies.
Depression manifests itself in one or more of the following ways: Insomnia, fatigue, loss of body weight, menstrual changes, sexual disturbances, palpitation, breathlessness. Gloom, anxiety, slowing down of mental and physical functions and avoiding people etc., are some of the symptoms.
Persons with suicidal tendencies need counselling.
Symptoms
Avoiding people, slowing down mental and physical functions, body weight loss, insomnia, menstrual changes, breathlessness, palpitation, fatigue, sexual disturbances, anxiety and gloom are the common symptoms and signs of depression.

11. Snoring
Problem
When a person makes an irritating rattling or rumbling sound during sleep, it is called snoring. It disrupts sleep for both the snorer and those present in the same room.
Symptoms
Sleep apnea (breathing repeatedly stops and starts throughout the night), disrupted sleep and morning headaches.

12. Bed-Wetting (Enuresis)
Problem
Bed wetting is normal during the first 2 to 3 years of life. If it persists later on, then it may be due to delayed maturity of the muscles and nerves of the lower urinary tract. The problem is often genetic and occasionally psychological.
The patient should not take sugar or any other sweets at night and should drink less quantity of water at night time.
Sugar in urine also should be checked if necessary.
Symptoms
Peeing in the bed and being dry during the daytime, pain while peeing and changes the colour of urine. Here, the symptoms depend on the causes.

13. Tennis Elbow
Problem
Tennis Elbow arises when the person gets a repetitive strain injury on the outside of the elbow. Here, the tendons on the forearms get damaged due to repeated motion and it is common in athletes.
Symptoms
Pain in the hands, especially in the morning and difficulty shaking hands, holding heavy objects, turning the knob, or even holding a cup of coffee.

14. Vertigo
Problem
Vertigo is a sensation of moving or spinning of one's own body or of surroundings, usually accompanied by nausea and loss of balance.
Dizziness, light headedness, a vague spaced out feeling and faintness also are experienced.
Organs have nerve connections with specific area of the brain. Many conditions can affect the inner ear and cause vertigo. Motion sickness is the most common cause. Such people feel especially dizzy in a moving car or a rocking boat. Drugs, circulatory problems and neurologic disorders, are other causes. Abnormal eye movements indicate a possible dysfunction of the inner ear or its nerve connections to the brain.
When the patient with vertigo wants to sleep, he should slowly lie down by turning on one side on the bed. Even while getting up from sleep, he should turn to one side and then slowly get up. If there is imbalance in the equilibrium of ear, then the house bell should be disconnected until the patient recovers.
Symptoms
The person might feel dizzy on a rocking boat or even in a moving car. Disturbed nerve connection between the inner ear and the brain results in abnormal eye movements.

15. Liver Problems
Problem
The liver is a vital organ that performs over 500 chemical functions. Moreover, it filters toxins from the blood, produces essential proteins and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Types of liver problems are hepatitis (liver inflammation), jaundice, liver cancer, Wilson’s Disease (accumulation of too much copper in the body), Cirrhosis (non-functioning liver) and Hemochromatosis (iron build-up).
Symptoms
The most common symptom of a damaged liver is yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice). Other symptoms are nausea and vomiting, fatigue, loss of appetite, abdominal pain or swelling, dark urine, pale stool, itchy skin and easy bruising or bleeding.

16. Menstrual Disorders
Problem
Menstrual disorders are the reasons behind the disturbed menstrual cycle in a female like irregular periods (periods coming early or sometimes it's late), heavy bleeding.
Symptoms
Irregular and painful periods, mood swings, nausea or vomiting or migraine with periods, fatigue or dizziness.

17. Multiple Sclerosis
Problem
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) influences the myelin sheath. Nerves are secured and smooth transmission of electrical signals is guaranteed by the myelin sheath. However, the nerve signals get harmed when the autoimmune attacks the myelin sheath in MS.
Symptoms
Muscle weakness, fatigue, numbness or tingling, vision problems, balance and coordination problems, speech problems, bladder and bowel and cognitive problems, mood swings, sexual dysfunctions and problems with the bladder and bowel.

18. Osteoarthritis
Problem
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative wear and tear process accruing in joints that are impaired by congenital defects, ageing, vascular insufficiency or previous disease or injury. It is the most common variety of arthritis. It frequently affects the spine. The lower limb joints are affected more often than the upper limb joints. There is no synovial thickening, no increased local warmth and no muscle spasm.
Conservative treatment such as local heat and appropriate muscle strengthening exercises may be given. Stretching, strengthening and postural exercises help to maintain healthy cartilage and increase a joint’s range of motion. Straight back chairs are to be used at all times.
Symptoms
Delicate and stiff joints, loss of flexibility, crackling or popping sound in the joint and pain in the affected joints.

19. Insomnia
Problem
Generally, a person gets unconscious in sleep but can be awakened via stimuli or senses. However, the person suffering from insomnia finds it hard to sleep or continue to sleep. Serotonin is the transmitter substance associated with sleep in the medulla.
Symptoms
People with insomnia wake up again and again at night. Similarly, they can wake up early in the morning and remain tired for most of the day. They get headaches, easily get irritated or depressed and find difficulty in concentrating on work.

20. Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Problem
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) affects the large intestine (colon). It is a chronic disease, but an appropriate treatment can improve the patient’s quality of life.
Symptoms
Bloating and gas, mucus in the stool, a feeling of incomplete excretion after a bowel movement, abdominal pain and urgency to have a bowel movement.

21. Alzheimer’s Disease
Problem
Alzheimer's Disease is a progressively neurodegenerative disorder that attacks an individual's memory and behaviour. Here, the cells in the central nervous system die. It represents the most common cause of dementia among people aged over 60 years. It is a progressive disease that destroys memory and other important mental functions.
Symptoms
Initially, it starts with symptoms such as mild memory loss, difficulty finding words, carrying out a conversation and making judgements. Then, the disease progresses and leads to severe memory impairment, confusion about the time and day, inability to perform familiar tasks and a difference in mood and personality.

22. Cerebral Palsy
Problem
Cerebral Palsy is a nonprogressive central motor deficit and it can be of spastic type. Congenital malformations of the brain, cerebral anoxia, trauma to the brain during birth and other prenatal and perinatal reasons lead to Cerebral Palsy. Further, C.P. might give rise to hemiplegia, monoplegia, paraplegia and quadriplegia.
Symptoms
A tilted pelvis, twisted neck, a curved spine, developmental delay, uncontrolled movements, spasticity, difficulty in carrying a conversation, intellectual disabilities, seizures and impaired vision and hearing.
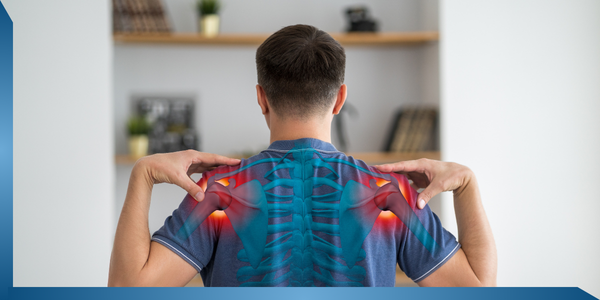
23. Cervical Spondylosis
Problem
Cervical spondylosis is characterised by degeneration of the intervertebral discs resulting in compression of nerve roots.
Pain arising from the cervical spine is felt in the neck and back of the head, though it may often be projected to the shoulder, arm and even forearm and hand. The pain is evoked or enhanced by certain movements or position of the neck and is accompanied by tenderness and limitation of movements of the neck.
Symptoms
Due to certain movements in the neck, pain arises in the arm, forearm, hand and shoulder. Thus, such patients can have only limited movements of the neck.

24. Spasticity
Problem
Spasticity is an increase in deep tendon reflexes and muscle tone. Like Hemiplegia, Spasticity can be a result of an upper motor neuron lesion. Here, the person loses control over the upper motor neuron. However, the muscles only become weak and not paralysed. The person might suffer involuntary body part movements or rigidity. For instance, a spastic kid might not hold his head straight.
Symptoms
Increased voluntary contractions of muscles due to stimulus, deformities in the joints, muscles or bones, abnormal posture, muscle stiffness and painful contractions.
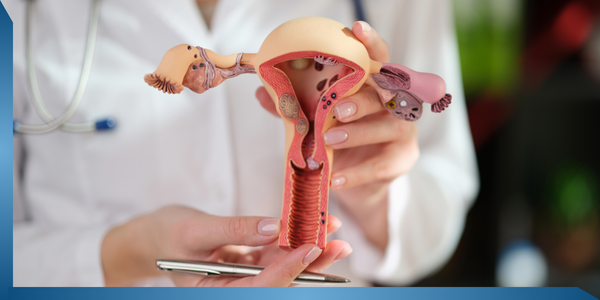
25. Prolapse of Uterus
Problem
Prolapse of the uterus is a condition in which the uterus or a part of it protrudes out of the vagina, due to a defective pelvic floor. In the early stages there is back pain while standing and on exertion. Other symptoms are frequency of urination and/or incontinence of urine. In the later stages a protrusion at the vulva is noticed. Sometimes leucorrhoea is also present.
Symptoms
The person might feel back pain while excreting or standing in the early stage. Other symptoms of the prolapse are uncontrolled urination, the uterus sticking out from the vulva (in a severe case) and a whitish or yellowish discharge from the vagina.

26. Writer’s Cramps
Problem
Writer’s cramps are the painful contractions in one or both hands. Thus, a writer might lose control over hand movements, typing and the ability to hold a pen.
Symptoms
Here, your hands might get numb and generate a tingling or burning sensation, stiffness or pain (with varying severity). In a severe case, your hands might turn red or get swollen.
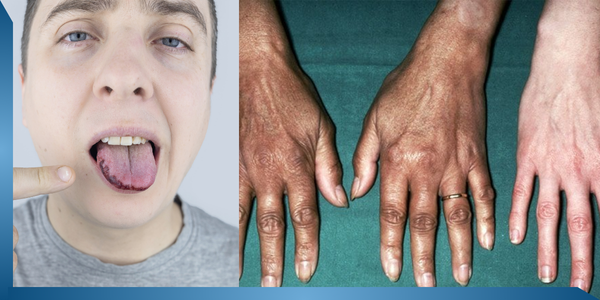
27. Addison’s Disease
Problem
Addison’s Disease (adrenocortical insufficiency) occurs when a person’s adrenal glands produce insufficient steroid hormones called Corticosteroids. Moreover, adrenal glands get destroyed when the person suffers from TB, cancer or other unidentifiable diseases or consumes Corticosteroids like Prednisolone. According to the scientists, 70% of the cases include destruction of the adrenal glands due to an autoimmune reaction.
Due to the hypoactivity of the adrenal medulla, one might suffer from low blood pressure. On the other hand, one may have increased ACTH production due to lower cortisol secretion. This ACTH directly affects the melanocytes and enhances melanin pigmentation.
Symptoms
Skin darkening (as if tanned), dizziness while standing, sitting or lying down, black freckles, kidney failure, weakness, tiredness, severe abdominal pain or shock. The body excretes more sodium and less potassium.

28. Angina/Ischemia
Problem
This is a short-term chest pain due to insufficient oxygen and blood flow to the heart muscle. The pain is mostly beneath the sternum (centre of your chest). The heart requires continuous blood supply to work normally.
However, the heart works harder during an emotional outburst or physical exercise, which increases its oxygen demand. Thus, the coronary arteries (that supply blood to the heart muscle) narrow down, resulting in insufficient blood flow and oxygen to the heart muscles. Ischemia without Angina is called asymptomatic or silent Ischemia.
Symptoms
Pressure or pain beneath the sternum or left shoulder or left arm, tightness, choking, tingling, toothaches, pain in the jaw, numbness of fingers, gas trouble, indigestion and discomfort in the neck and shoulder blades. Pain might be more in the cold weather.
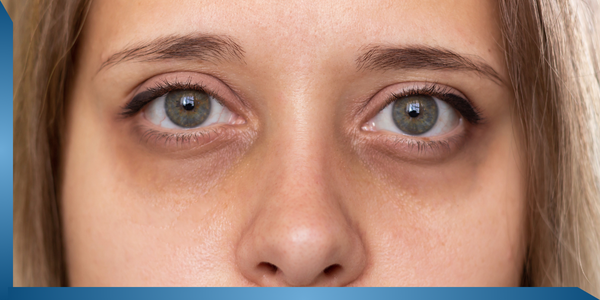
29. Black Rings Around Eyes
Problem
The skin under the person’s eyes gets darker than the skin on the face. Low blood pressure, excessive white discharge, anemia and sleeplessness are the common causes of black rings around the eyes.
Symptoms:
Eye strain, tiredness, puffiness around the eye area and itchy eyes.
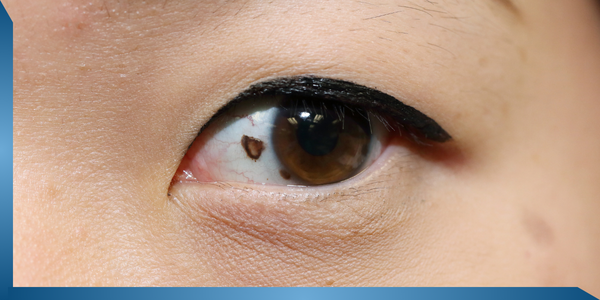
30. Sty in Eyes
Problem
Sty in the eyes are caused due to Vitamin A deficiency.
Symptoms:
You might witness threads, lines or dark spots before the eyes. There’s no need to worry until they bother continuously.
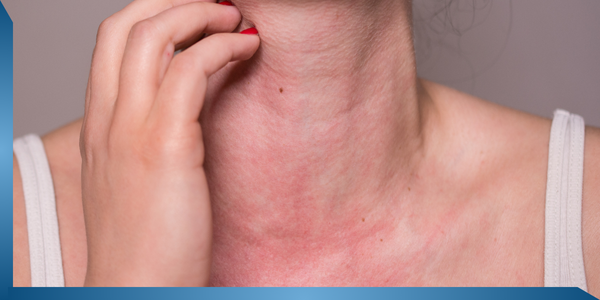
31. Allergy
Problem
The most common symptoms are itchy and running nose, vomiting, hives, stomach cramps, sneezing and red, watery, itchy or swollen eyes.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms are sneezing, red, watery or swollen eyes and more.

32. Chronic Constipation in Children and Adults
Problem
Constipation is a common problem where the person might have less than three bowel movements in a week. It might occur due to acidity or hypothyroidism. Moreover, it leads to fissures and piles.
Symptoms
Straining in the toilet, incomplete excretion, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, bloating, nausea or throwing up.

33. Down’s Syndrome (Mongolism)
Problem
People with the chromosomal disorder, Mongolism, have delayed mental and physical development. They have an average IQ of 50 (while others have 100) and rarely cry. This chromosomal disorder results in mental retardation and physical abnormalities.
Symptoms
They are quiet and have floppy muscles, small and low set ears, short and broad hands, a bony pelvis, underdeveloped genitalia, a single crease across the palm, small eye orbits, skull and eyes and tongue protrusion. They can have congenital cardiac defect and their fingers can easily bend backwards.

34. Dryness of Eyes
Problem
Dryness of the conjunctiva (a thin membrane that protects your eyeball). Ageing, reduced secretion of tears from the lacrimal gland, hormonal changes, poor blinking habits, menopause or a dry environment cause dryness of the eyes.
Symptoms
A scratchy or burning sensation in your eyes, less mucus around your eyes, eye redness and difficulty driving at night or wearing contact lenses.

35. Diabetes Mellitus (Glycosuria)
Problem
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a common endocrine disease and in some people, it is purely genetic. Such people have abnormally higher amounts of glucose in their blood. The main two types of diabetes are:
- In Type I diabetes, also called Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM), the pancreas secretes a lack of insulin.
- In Type 2, the body cells resist the effect of the normal levels of insulin manufactured by the pancreas. This type is also called Non-insulin Dependent Diabetes (NIDM).
Symptoms
People with diabetes feel more thirsty and exhausted, have weight loss with an increased appetite and their wounds don’t heal quickly. Such people complain of an increased frequency of micturition, especially at night.

36. Hole in the Heart
Problem
Some people carry a hole in the heart right from birth and this disease has 3 types:
- The Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) is a hole between the left and the right ventricles, which should have been closed right after birth.
- Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) is an abnormal opening of the two atria connected by the foramen ovale that should have been closed after birth.
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) is the communication between the pulmonary artery and aorta in newborn babies. The ductus arteriosus blood vessel should close within 24 to 48 hours of birth, and if it does not close, it is called PDA.
Symptoms
Children with a hole in the heart experience a skipped heartbeat, easy tiring, shortness of breath and swelling of the belly area, feet and hands.

37. Eczema
Problem
In general, eczema is a superficial inflammatory process involving primarily the epidermis, marked initially by redness, itching, minute papules and vesicles, oozing and crusting and later by scaling and often pigmentation. Eczema is localised to certain parts of the body.
Symptoms
Skin becomes dry, itchy, red and pigmented and minute papules and vesicles are formed. These papules and vesicles may crust or ooze and lead to scaling. It occurs only in specific parts of the body.

38. Frequent Urination
Problem
Under frequent urination, the person gets an urge to urinate frequently though the total daily amount of urine does not increase. Frequent urination happens due to a weak bladder or a bladder infection. In some males, it can be a result of an enlarged prostate gland. A weak bladder cannot store more urine which causes urination in small amounts.
Some people might suffer from frequent urination at night. It is called ‘Nocturia’ and is a result of heart problems, diabetes, early stages of kidney disease, intake of more fluids or liver failure.
Symptoms
Such a person must seek professional help if these symptoms with frequent urination are found: pain while passing urine, pain in the groin, dark brown urine or the presence of blood in urine.

39. Infertility in Men
Problem
Infertility in men means disrupted normal sexual and reproductive functions. It may result from psychiatric, endocrine, vascular and neurologic diseases.
Symptoms
Difficulty in ejaculation and erection, swelling in the testicle and loss of interest in intercourse.

40. Hypoparathyroidism
Problem
In hypoparathyroidism, nails become brittle and ridged and may fall off. Hair tends to become dry and sparse. Fissures are seen at right angles of the mouth. It refers to hypocalcaemia.
In hypocalcaemia, the parathyroid glands do not function properly and therefore, there is deficiency of blood calcium. It is characterized by muscular twitchings and convulsions, particularly of the hands and feet.
Symptoms
Its symptoms include ridged (lines on the nails) or brittle nails that might fall off, dry and sparse hair and fissures at the right angles of the mouth.

41. Stammering
Problem
Stammering or stuttering is a speech problem characterized by involuntary pauses while speaking, often with repetition of sounds. It may be a genetically transmitted nervous disorder.
Symptoms
Repeating sounds, prolonged sounds, pausing while speaking, anxiety about speaking, avoidance of certain words and eye blinking.

42. Hydrocele
Problem
Hydrocele is a disorder where fluid accumulation occurs in the scrotum, along the spermatic cord. Hydrocele can also be a result of hypothyroidism.
Symptoms
One or both testes swell and the scrotum feels heavy and painful. The size of the scrotum might increase later in the day.

43. Migraine
Problem
Migraine is more common in women. Here, the person suffers repetitive intense pain in one or both sides of the head. Here, the arteries to the brain get contracted due to abnormal blood levels of serotonin. Sleeping and dark surroundings can help a person suffering from migraine get relief.
Symptoms
Migraine shows gastrointestinal symptoms and disturbance in the nervous system. It also shows symptoms 10 to 30 minutes before its arrival (this period is called aura or prodrome). For instance, the person gets irritated, depressed, restless and experiences loss of appetite, sensitivity in the scalp and nausea for about 20% of the people. Some people might even lose vision in a specific area.

44. Motor Neuron Disease
Problem
Adult males above 40 specifically suffer from Motor Neuron Disease which causes progressive degeneration of the corticospinal tracts, the anterior horn cells of the spinal cord and brain stem motor nuclei.
Symptoms
This disease leads to other diseases as symptoms. For instance, such patients might develop problems in speech and movements, muscle stiffness, clumsiness, spasticity, drooling, joint pain and more.

45. Infertility in Women
Problem
Infertility addresses the inability of women to conceive a child.
Symptoms
Longer, shorter or irregular menstrual cycles, pain during intercourse, hormonal imbalances and pale or dark menstrual blood.
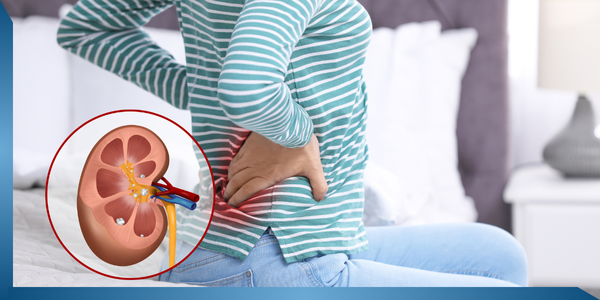
46. Nephritis
Problem
Nephritis is a condition where the tissues of both kidneys get inflamed and have a disturbed blood purification process. It can be chronic or acute.
Symptoms
Change in urine colour and habits, pain in the pelvis, foamy and blood in the urine and swollen body parts. Other symptoms include fever, headache, high blood pressure or edema

47. Obesity
Problem
Adipose tissues store food energy as fats. Because of this storage, an individual of normal weight can survive for two months of total starvation. Assessment of skin-fold thickness over various areas of the body together with height, weight and age can be used to assess the degree of adiposity. Obesity is best defined as any degree of adiposity that leads to health problems.
To some extent, appetite is controlled by some discrete areas of the hypothalamus. Secondary obesity may be because of hypothyroidism which causes a decrease in the metabolic rate.
Calory restriction is the basis of weight reduction. Once obesity occurs, it is a lifelong chronic illness requiring continuous treatment, even after weight loss has occurred. One method of finding whether a person is obese is by the 'body mass index' formula (BMI).
BMI for both men and women should not be less than 18. Otherwise anaemic conditions will be created.
Symptoms
Obesity is itself a symptom of excessive body fat. However, snoring due to obstructed airways, swollen and twisted veins due to poor blood circulation, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, heart diseases and more are the effects of obesity.
48. Osteoporosis
Problem
Senile or idiopathic osteoporosis is of unknown cause. It affects older women more than middle-aged people. Moreover, women with an inactive lifestyle have a higher risk of Osteoporosis. Senile means the characteristic of old age. Osteoporosis is a decrease in the density of bones. People cannot notice it early but there comes a point when even small activities like coughing cause a fracture due to the reduced density of the bones.
For the body to absorb calcium from food and incorporate it into the bones, it needs a sufficient amount of calcium, other minerals, and the right amounts of several hormones, including parathormone, growth hormone, calcitonin, oestrogen in women, and testosterone in men. Moreover, Vitamin D is required to absorb calcium from food and use it for the bones.
A fracture is mostly caused in the spine, hip and wrist. An injury to the spine causes a humped back. Thus, weight-bearing exercises, climbing the stairs, walking, proper diet and maintaining strong bones by 35 are the preventive measures.
Symptoms
Fractures in the vertebrae and other bones and inability to stand erect.

49. Myoclonus and Hiccups
Problem
Our muscles get sudden, involuntary synchronous muscle jerks or twitches. It is called myoclonus. It is a result of quick muscular contraction and relaxation. When air enters the trachea through the half-closed glottis (opening between the vocal cords) a noise occurs. Those are the hiccups. So a hiccup is a form of myoclonus and occurs in the diaphragm.
A person swallowing a lot of pungent or irritating food or drink might get a bout of hiccups. Hiccups stop when carbon dioxide accumulates in the blood. You may hold your breath or pull on the tongue to stimulate the vagus. However, hiccups caused by tumours are difficult to stop.
Symptoms
People with a tumour have hiccups with long bouts that do not stop easily. Other symptoms are possible slight discomfort or mild pain in the chest or abdomen, temporary disruption in breathing pattern and more.

50. Bronchitis
Problem
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchi, usually caused by an infection, or by irritants such as smoking, air pollution etc., or by allergens. Acute bronchitis is acute infection of the mucous membrane of the trachea and bronchi and is produced by viruses, bacteria or external irritants. Fever, cough, choked-up feeling are some of the common symptoms. In chronic bronchitis, cough is due to excessive mucus secretion in the bronchial tree. Bronchi are narrowed by infected mucus. It is worst in winter.
Cough may be dry or with expectoration. Rest in bed, light diet and small quantities of frequent fluid diet is recommended.
Symptoms
Fever, wheezing, cough, runny or stuffy nose, fatigue, shortness of breath, sputum in the cough, fever and choked-up feeling.

51. Diarrheoa/Dysentery
Problem
Diarrhoea is frequent passage of watery stools. In dysentery, there is mucus or blood present in stools. Patient may have colicky pain. Infection of colon or small intestines may be due to contaminated food, water or cold drinks.
Due to loss of alkaline upper intestinal secretions in stools, Acidosis occurs.
Symptoms
A colicky pain is the most common symptom. Some symptoms before diarrhoea are cramps in the belly, bloating and rushing for a bowel movement.

52. Hair Falling (Alopecia)
Problem
Hair fall may occur due to thyroid or pituitary deficiency, after a severe illness with high fever, excessive use of some drugs or protein deficiency. Thus, drink a lot of water and ensure your diet has more proteins.
Symptoms
Bald patches, tenderness, itching, stinging and burning sensation in the scalp, especially in the affected area.

53. Muscular Dystrophy
Problem
In progressive muscular dystrophy there is weakness of legs and hands. Slurring of speech is also experienced.
In the first stage, there is atrophy of intercarpal muscles of thumb and the first finger. In the next stage, the tongue of the patient cannot move properly. He cannot take the tongue out. At a later stage he cannot even swallow. There is more saliva in the mouth. Whatever he eats, may go into the trachea. In such a case, pat the patient behind the neck and by thumping try to take out the object obstructing the air passage.
Symptoms
Muscle pain and stiffness, frequent falls, trouble running and jumping, stiff or loose joints, difficulty walking, trouble swallowing, fatigue, spasticity and more.
Enjoy the Gift of Life and Don’t Let Your Body Be a Puzzle to You

FAQs
SEO Part
neurotherapy treatment in Malad
neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad
neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad
neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad
neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad
neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad
neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in maladneurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in maladneurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in maladneurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in Malad, neurotherapy treatment in malad